Automatic Position Reporting System for HF
APRS Network
The Automatic Position Reporting System (APRS) network comprises:
- RF User - Equipped with a base station transceiver and APRS Terminal Node Controller (TNC)
- Portable User - Equipped with an APRS-compatible Hand-Held radio
- Mobile User - Equipped with a mobile transceiver and APRS TNC
- Weather Station - Conneted via the Ineternet
- Fill-In Digipeater - Provides extra coverage for a Wide Repeater
- Wide Digipeater - Wide area node
- IGate - Equipped with a base station transceiver, APRS TNC and Internet connection
- APRS Database and Web Server - APRS Internet Service (APRS-IS)
- Internet User - Mobile Device with APRS app connected to the Internet
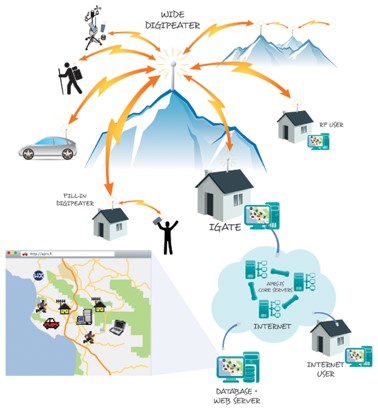
The APRS Network
APRS Description
The APRS defines:
- Stations, for broadcasting location, telemetry data, text over both RF and Internet networks
- Nodes, which are identified by Callsign-SSID format
- Each node can store and forward messages
- Messages, which are unnumbered AX.25 datagrams
- The message “Path” contains a routing list
- Digipeaters modify the Path to avert the “ping-pong” effect
APRS Secondary Station ID (SSID)
Each APRS node uses a callsign with a SSID suffix, identifying its purpose:
-0 (No SSID) Home Station-1 Digipeater, or Home Station running a Fill-In Digi,-2 Digipeater [#2] on 70CM-3 Digipeater [#3]-4 HF to VHF Gateway-5 IGate (Dedicated system, not home station)-6 Operation via Satellite-7 Kenwood D7 Handheld-8 Secondary Mobile usage (also Maritime vessels) (VHF / UHF)-9 Mobiles (VHF / UHF)-10 Operation via Internet Only (No RF capability)-11 is for APRStouch-tone users (also high altitude balloons)-12 Portable Units such as Laptops, Camp Sites etc-13-14 Interstate Truckers-15 Operation via HF
APRS Paths
The APRS path is a routing list for the message: VK3ABC-1, VK3XYZ-1, etc
- Can use callsign aliases for special nodes: WIDE1-1, WIDE2-1
- The SSID of aliases sets the number of hops allowed
- The path is modified by each digipeater
- The SSID is decremented in each hop, but -0 is omitted.
- An asterisk (*) signifies when a callsign or alias was used
- Example:
- WIDE1-1, WIDE2-2 (Original path)
- <callsign1>*, WIDE2-2 (First hop)
- <callsign1>, <callsign2>, WIDE2-1* (Second hop)
- <callsign1>, <callsign2>, <callsign3>* (Third hop)
APRS Rules for HF
There are special rules for APRS used on HF, primarily because HF, unlike VHF/UHF, presents a very wide area network.
- No Digipeating on HF!
- Most receiving Gateways will route to APRS-IS
- So, Path = WIDE1-1 is sufficient
- Use 300 Baud, 200Hz FSK, 1600Hz/1800Hz
- For SSB must be spot on frequency
- LSB & USB both work because AX.25 is NRZI
- Avoid any ALC action on TX to limit distortion
- Beacon time ≥ 10 minutes: Permits up to 70 users
- Good luck – Because APRS has no ACK or FEC
APRS Frequencies and Gateways
There are defined frequencies used for APRS. However the APRS stations may change over time.
40m 7048.600kHz LSB
VK2IO-4 Sydney Primary Net Station (also 7.047.17 LSB)VK7HSE-4 Kingston Secondary Net Station
30m 10147.600kHz USB
VK1IAN-1 Canberra RX OnlyVK2ACW-1 OrangeVK2HL-1 Sydney Part Time RX OnlyVK2IO-4 Sydney OfflineVK2OL-5 Sydney Full Time RX OnlyVK2ZSZ-4 Queanbeyan Full Time RX OnlyVK2ZZM-5 Sydney Full Time RX OnlyVK3MY-4 Melbourne Primary Net stationVK4AB-4 Ipswich Full TimeVK4DMI-4 Pine Rivers Secondary Net stationVK4MQ-5 Toowoomba Full Time RX OnlyVK4RM-4 Mackay Full TimeVK4UN-4 Tewantin Full TimeVK5RR-4 WaikerieVK6LD-4 Perth Full TimeVK7ZRO-4 Bothwell Full TimeVK8KMD-10 Alice SpringsZL3GR-4 Tauranga RX Only
20m 14103.00kHz LSB
VK2IO-4 Sydney Offline
APRS TNC Pin Assignments
We use an Argent Data Systems T3 Mini TNC board. This is an excellent device with a good configuration tool. It has a wide variety of input/ouput pins, suitable for communications, control and telemetry.
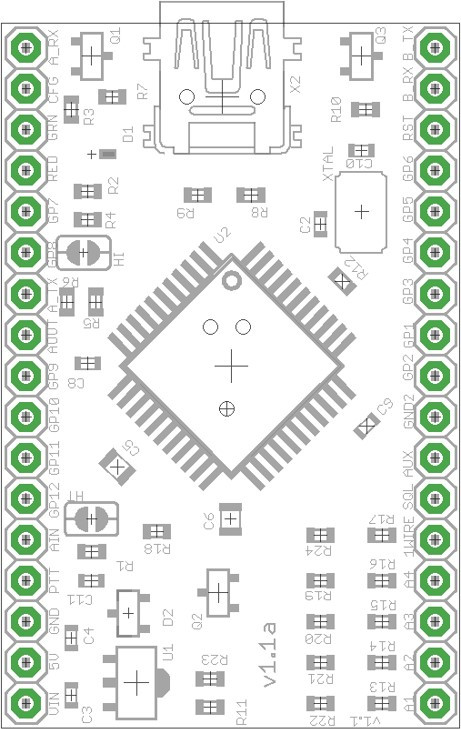
Argent Data Systems T3 Mini TNC
Pin Assignments:
- A1-A4 Analog inputs 1-4 (max voltage 4xVdd)
- 1W Dallas 1-Wire data bus
- SQL Squelch input
- AUX Auxiliary I/O pin
- GND Ground
- RST Reset (active low)
- B-RX Serial port B input
- B-TX Serial port B output
- A-RX Serial port A input
- A-TX Serial port A output
- CFG Configuration select
- AOUT Audio output (to radio)
- AIN Audio input (from radio)
- GRN Green LED output for external LED
- RED Red LED output for external LED
- PTT Push-to-talk (open collector)
- 5V Regulator output or Vdd input, 5v max, 2.8v min
- VIN Unregulated supply voltage, 6v to 28v
- GP1-GP12 General purpose digital input/output pins
TNC Configuration Tool
Argent Data Systems T3 Mini TNC board comes with OpenTracker - a versatile configuration tool.
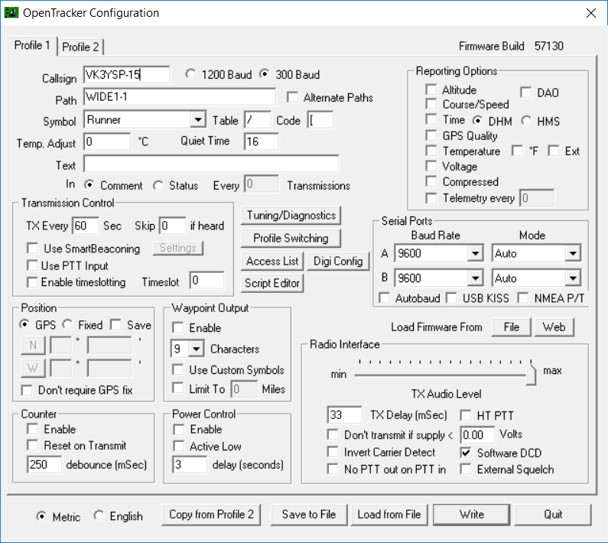
OpenTracker TNC Configuration Tool
APRS TNC Wiring
The Argent Data Systems T3 Mini TNC board connects directly to a Serial TTL GPS Receiver. We use solderable enamelled copper wire to interconnect such devices.
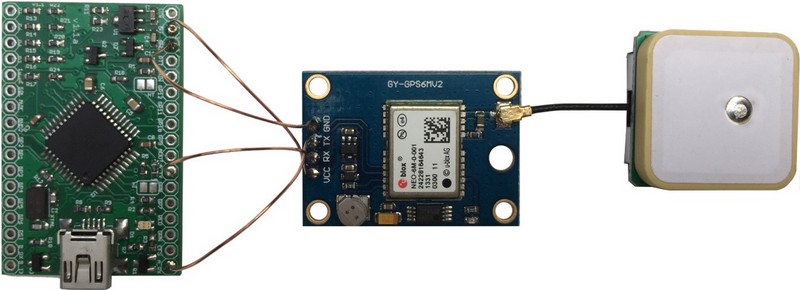
Argent Data Systems T3 Mini TNC - Ublox NEO-6M GPS Receiver - GPS Patch Antenna
A 5V regulator and two audio line transformers complete the design for connecting the TNC to a radio transceiver.
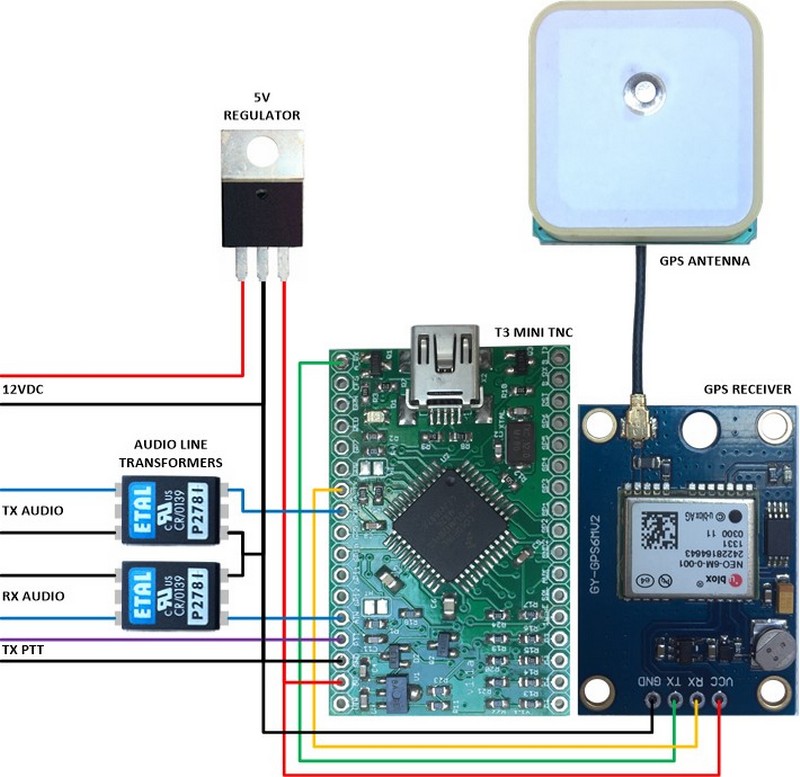
Pictorial Schematic Diagram
APRS TNC Assembly
The components are assembled into a Hammond H9004 ABS Enclosure. The transformers and regulator are glued to the base. A sleeved grommet is used for the CAT-5 cable.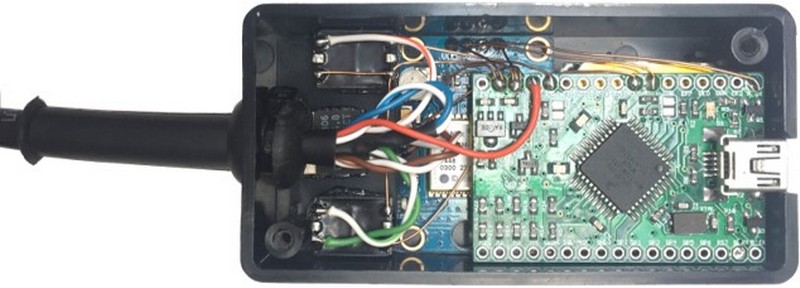

APRS TNC Assembly 1
The completed APRS TNC dongle needs to have a clear view of the sky. It will starts transmitting when a 3D GPS fix is valid.

APRS TNC Assembly 2
APRS Display
The resulting APRS data, relayed to the Internet by an IGate, is easily displayed on the aprs.fi website.
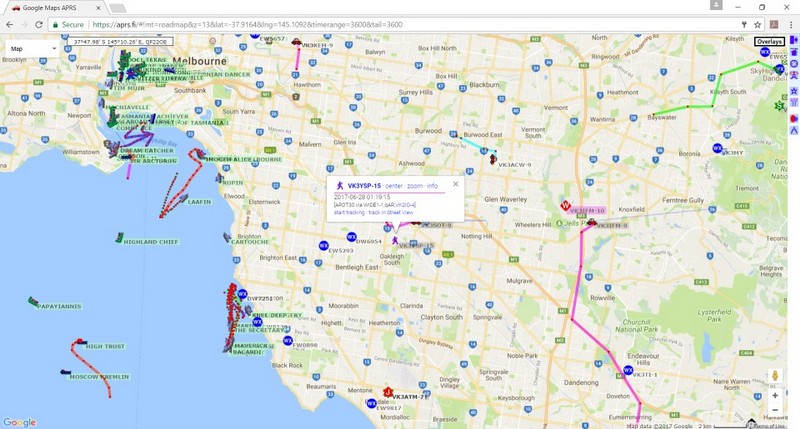
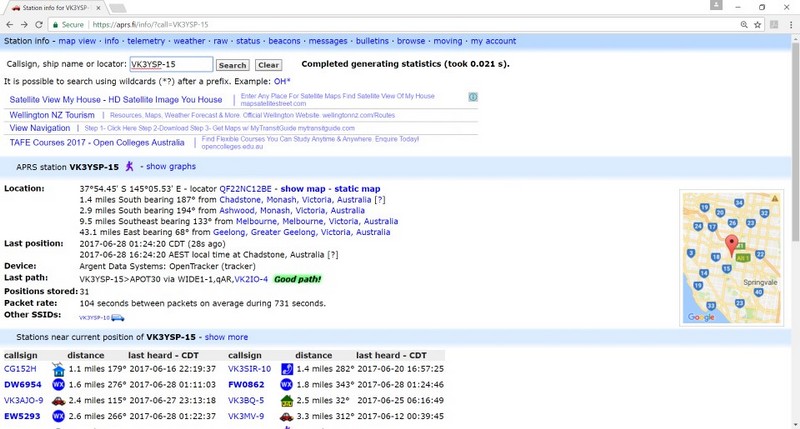
APRS Station Info
By querying the aprs.fi website additional station information can be displayed.
References
- APRS GippsTech 2017 Presentation
- http://www.aprs.org
- http://www.aprs.net.au
- https://info.aprs.net
- https://aprs.fi
- https://www.argentdata.com